對外服務
即時訊息
最新消息
2026-01-13 2026年農曆春節期間生資中心暫停服務公告
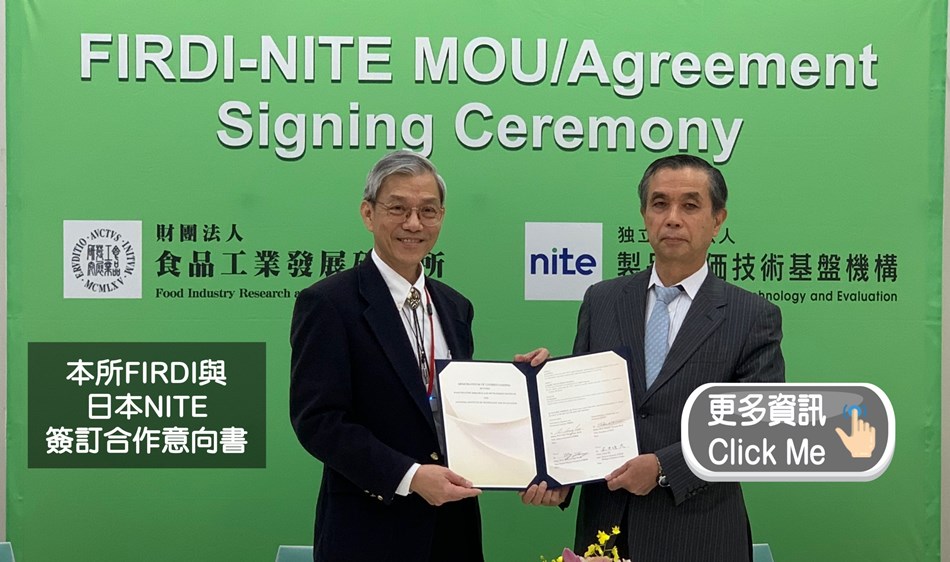
2025-12-18 食品所生資中心獲 TAF 認證為【全國首家取得 ISO 20387 認證之生物資料庫】
2025-10-28 生物資源線上目錄暫停通知(2025-11-07)
2025-10-16 【細胞寄存限時活動】- 細胞庫核心設施提供『免費細胞公開寄存』服務
+更多資訊
網頁新知
2026-01-26 非侵入性大腸癌篩檢之新途徑
2026-01-12 大腦鋰缺乏可能導致阿茲海默症?
2025-12-28 以球形紅桿菌萃取物作為細胞培養系統替代補充劑的潛力
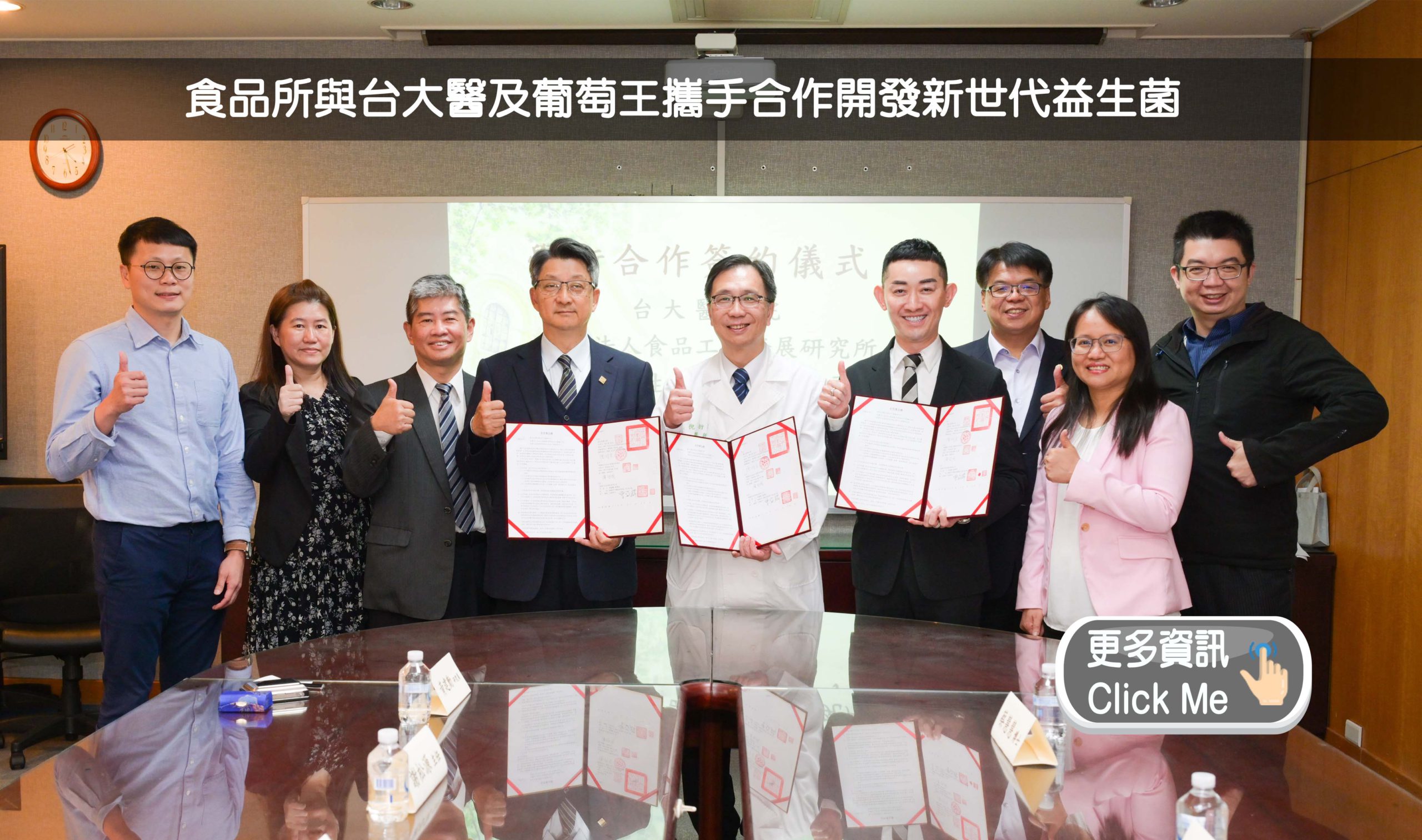
2025-12-08 臺灣第一株具改善腸道發炎潛力的本土Akkermansia次世代益生菌:食品所、國衛院與成大之合作
2025-12-07 永續建材:以真菌菌絲體作為微生物礦化支架
+更多資訊
生資中心簡訊