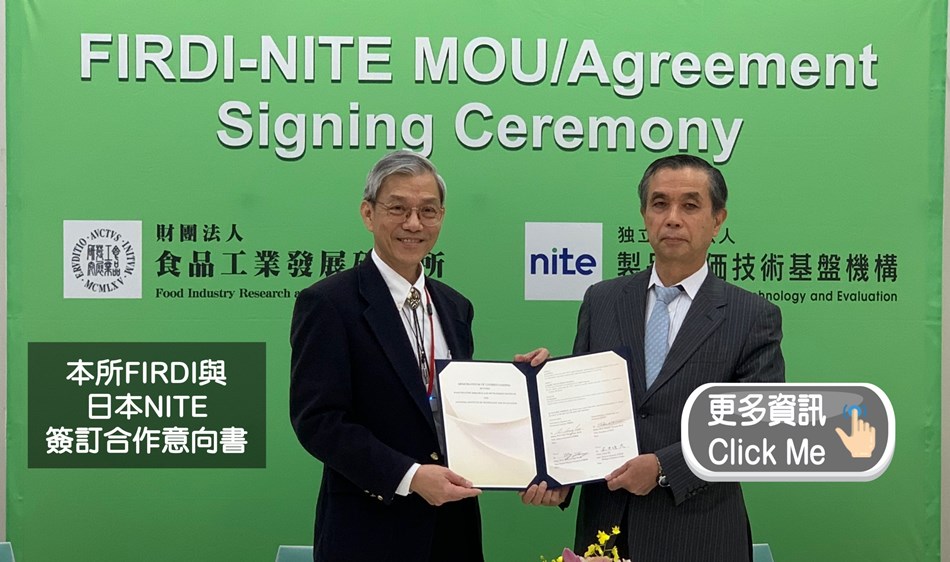
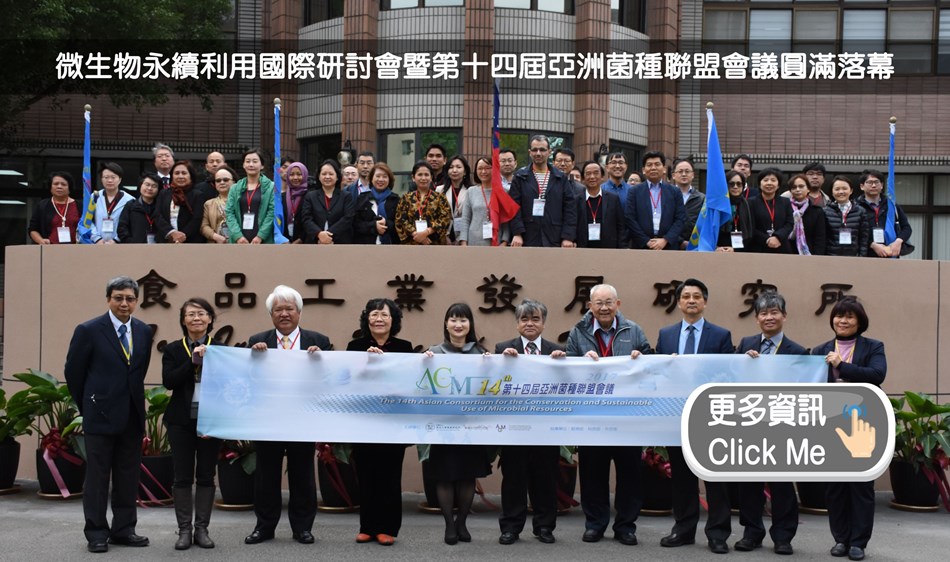
對外服務
即時訊息
最新消息
2025-03-24 114年清明節連假細胞株暫停出貨一次
2025-03-20 敬邀參與食品所114年研發成果展示暨產研合作計畫說明會
2025-02-26 114年度經濟部智慧財產局指定專利生物材料之國內寄存機構為財團法人食品工業發展研究所
2025-01-09 114年農曆春節期間生資中心暫停服務公告
2024-12-19 生物資源線上目錄暫停通知
+更多資訊
網頁新知
2025-06-30 基因編輯香蕉:告別爛果宿命,解鎖全球糧食新篇章
2025-06-09 益生菌對創傷性腦損傷後神經保護與腸道菌相之效應
2025-06-09 生物樣本庫,讓世界更健康
2025-04-29 LINE的AI助理服務 -「AI小幫手」
2025-04-29 腫瘤生態系中的隱藏玩家—真菌
+更多資訊
生資中心簡訊